UNDERSTANDING THE CREDIT SCORE IMPACT ON HOME LOAN INTERST RATES
Introduction
If you’re considering applying for a mortgage , it’s important to understand the significant influence your credit score can have on the mortgage rate you’re offered. In this blog post, we will explore how the credit score affects the relationship between interest rates and your overall loan costs.
Before we delve into the details, let’s establish some key assumptions that will be used to illustrate the impact of credit scores on your mortgage rate.
We will assume a property value of $750,000 and a loan amount of approximately $500,000.
The focus will be on comparing FICO credit scores of 720 and 660. It’s important to note it should be a FICO score because the credit reporting agencies have their own credit scoring models that can produce similar scores. Know which score is on your credit report.
For this analysis, we will consider a rate and term refinance for a conventional mortgage, which is guaranteed by Fannie Mae or Freddie Mac.
Additionally, we will assume a 30-day lock-in period and a 30-year fixed-rate mortgage.
Our example will revolve around refinancing a single-family residence.
Keep these assumptions in mind as we explore the numbers.
Now, let’s take a look at a rate sheet based on the aforementioned assumptions, with a particular focus on a FICO score of 720.
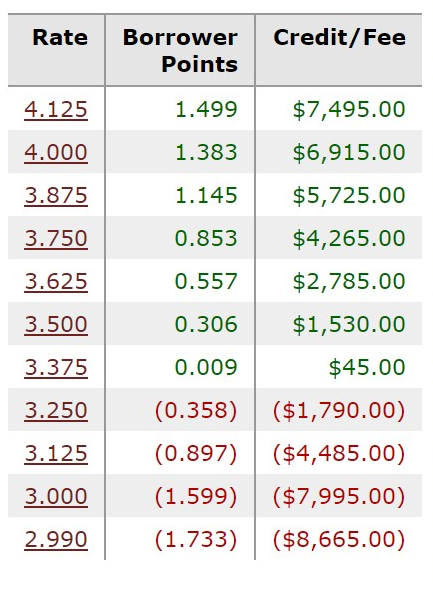
It’s essential to note that the range between 3.25% and 3.375% represents a critical break-even point. This is the threshold at which you transition from receiving a credit from the lender to having to pay points.
The credit is used to offset any closing costs associated with the loan transaction. As you move up from 3.375% to 4.125%, you’ll notice various credits available, such as $7,400 at 4.125% and $5,700 at 3.875%.
However, when you move down from 3.25%, you not only pay for your closing costs but also incur bonafide discount points or points. These terms essentially refer to the amount you must pay upfront to secure a loan at a specific interest rate.
For instance, at 3.25%, you may be required to pay $1,790 in addition to other affiliated costs. The relationship is clear: as rates increase, you receive more credits, but as rates decrease, you may need to pay points to secure the desired rate.
Now, let’s shift our focus to the impact of a FICO score of 660 on mortgage rates.
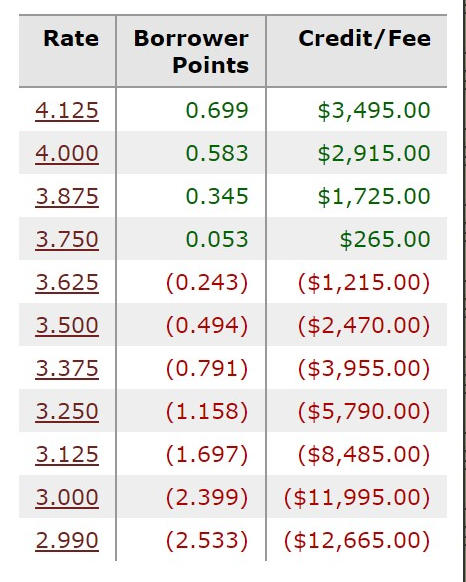
Looking at the table, you’ll notice that the break-even point has shifted upward when compared to a FICO score of 720. Instead of receiving a credit at 3.375%, the last of the credits now occurs at 3.75%.
This shift means that individuals with a 660 score will face higher rates compared to those with a 720 score. The basis for this discrepancy lies in the fact that at 3.375%, a borrower with a 720 score receives a credit, whereas someone with a 660 score will not. This disadvantage is a direct result of the 60-point drop in the credit score.
Key Takeaways
It’s worth noting that a drop in credit score can have additional financial implications beyond the interest rate itself. For example, let’s consider an interest rate of 3.125%. For an individual with a 720-credit score, the cost is slightly over $4,400. However, for someone with a 660-credit score, the 60-point drop in score translates to an additional cost of $4,000. This example underscores the importance of maintaining a good credit score to minimize the financial burden of a mortgage.
It’s crucial to understand that while both individuals in our example are eligible for the same interest rates, the difference lies in the amount of credit or points required to secure their desired rate.
It is a common misconception that individuals with a higher credit score above 720 will never have to pay points. In reality, circumstances may vary, and even borrowers with higher credit scores may need to pay points, albeit possibly fewer points compared to those with lower scores.
Conclusion
In conclusion, your credit score plays a significant role in the interest rates you are quoted when applying for a mortgage. A lower credit score can lead to higher rates, resulting in increased costs over the life of the loan. It’s crucial to carefully evaluate the costs associated with different interest rates and credit scores before making any decisions.
By understanding how credit scores impact mortgage rates, borrowers can take steps to improve their creditworthiness and secure more favorable terms on their mortgage. Remember, even with a credit score above 720, there may still be circumstances where points need to be paid.
Take the time to review your credit score along with your credit history, consider credit-building strategies, and work towards achieving the best possible terms for your home loan.
If you found this information valuable and want to discuss your scenario, please consider scheduling a free consultation.